Introduction
AI agents are quickly becoming one of the most transformative tools in technology. Unlike traditional software, these systems can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take action — all without explicit step-by-step programming. Whether answering customer questions, detecting security threats, or analysing massive datasets, AI agents can work tirelessly in the background or respond instantly to user input.
In this post, we’ll explore what AI agents are, the types and benefits of using them, and walk through a practical example of building one with n8n and LangChain — giving you a blueprint to start creating your own.
What are AI Agents and how do they work?
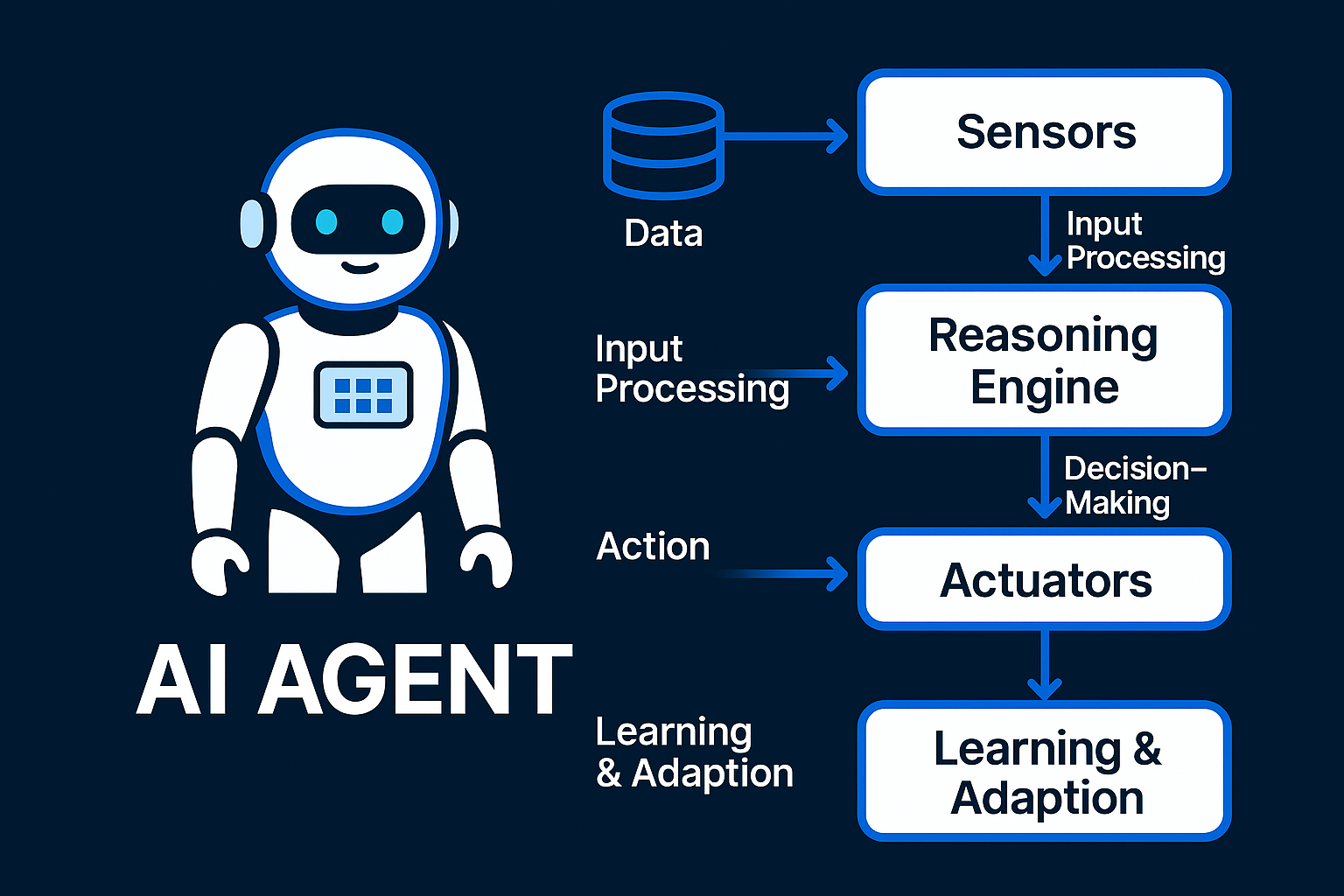
An AI agent is an autonomous system that:
- Receives data (via sensors like text, images, or system events)
- Processes inputs through a reasoning engine (often a Large Language Model)
- Takes actions (via actuators such as API calls or database queries)
- Learns and adapts over time based on feedback.
Modern AI agents use LLMs to understand natural language, chain prompts for multi-step reasoning, and produce structured outputs that can trigger workflows in other systems.
Types of AI Agents
- Simple Reflex Agents – React to the current situation without memory.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents – Maintain an internal model of the world.
- Goal-Based Agents – Plan steps toward a defined objective.
- Utility-Based Agents – Optimise for the “best” outcome based on multiple factors.
- Learning Agents – Improve over time through feedback and adaptation.
Most real-world LLM-powered agents combine aspects of all these types.
Benefits of AI Agents
According to LangChain’s State of AI Agents report, 51% of companies already use AI agents in production, delivering benefits such as:
- Faster decision-making – Automating research and analysis.
- Higher productivity – Freeing teams from repetitive tasks.
- Better customer experiences – Instant, 24/7 responses.
- Accelerated development – Supporting coding, debugging, and documentation.
- Improved data quality – Enforcing consistency and catching errors early.
How to build an AI Agent with n8n and LangChain
1. Define the Purpose
Decide what your agent should do (e.g., analyse sales data, handle customer tickets) and outline its core components — LLM, memory, and reasoning logic.
2. Set up your environment
Use n8n (self-hosted or cloud) to orchestrate workflows and integrate tools.
3. Prepare your Data
In the example from the guide, an SQLite customer database is downloaded, extracted, and stored locally.
4. Connect the LLM via LangChain
- Use the LangChain SQL Agent node to query your database.
- Add memory (e.g., Window Buffer Memory) to keep context between queries.
- Choose your model (like
gpt-4-turbo) and set the temperature for the output style.
5. Test and improve
Ask natural-language questions like “What are our top-selling products?” and refine the prompt or pass the database schema for efficiency.
Outro
AI agents aren’t just a futuristic concept — they’re already reshaping industries. With frameworks like LangChain and workflow tools like n8n, you don’t need to be an AI researcher to build one. The key is starting small: define a clear purpose, connect the right tools, and iterate with real-world feedback.
The same core principles apply when building a customer service assistant, a data analyst, or an autonomous system monitor. The sooner you start experimenting, the sooner you can put these digital teammates to work.